ICANN (short for Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) is a non-profit organization tasked with providing guidance and policy around the internet’s unique identifiers (domains). It was chartered in 1998. Prior to 1998, Network Solutions operated the global domain name system registry under a subcontract from the United States Defense Information Systems Agency.
You can search the list of domain registrars here: https://www.icann.org/en/accredited-registrars.
Microsoft
In addition to choosing a third-party registrar, organizations may also wish to use Microsoft as the registrar. Depending on your subscription, you may have direct access to purchasing domain names from within the Microsoft 365 admin center, as shown in Figure 1.4:
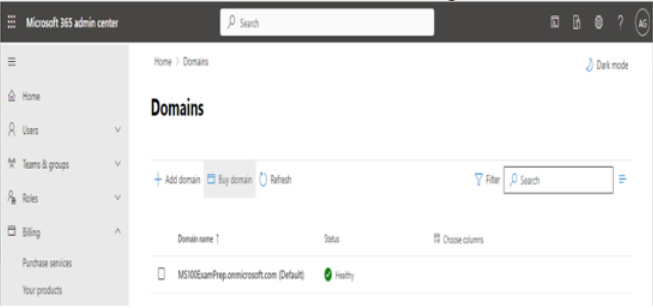
Figure 1.4 – Purchasing a domain through the Microsoft 365 admin center
When purchasing a domain through Microsoft, you can select from the following top-level domains:
- .biz
- .com
- .info
- .me
- .mobi
- .net
- .org
- .tv
- .co.uk
- .org.uk
Domain purchases will be billed separately from your Microsoft 365 subscription services. When purchasing a domain from Microsoft, you’ll have limited ability to manage Domain Name System (DNS) records. If you require custom configuration (such as configuring an MX record to point to a non-Microsoft 365 server), you’ll need to purchase a domain separately.
Configuring a domain name
Configuring a domain for your tenant is a simple procedure and requires access to your organization’s public DNS service provider. Many large organizations may host DNS themselves, while other organizations choose to pay service providers (such as the domain registrar) to host the services.
In order to be compatible with Microsoft 365, a DNS service must support configuring the following types of records:
- CNAME: Canonical Name records are alias records for a domain, allowing a name to point to another name as a reference. For example, let’s say you have a website named www.contoso.com that resolves to an IP address of 1.2.3.4. Later, you want to start building websites for na.contoso.com and eu.contoso.com on the same web server. You might implement a CNAME record for na.contoso.com to point to www.contoso.com.
- TXT: A Text Record is a DNS record used to store somewhat unstructured information. Request for Comments (RFC) 1035 (https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc1035) specifies that the value must be a text string and gives no specific format for the value data. Over the years, Sender Policy Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), and other authentication and verification data have been published as TXT records. In addition to SPF and DKIM, the Microsoft 365 domain addition process requires the administrator to place a certain value in a TXT record to confirm ownership of the domain.
- SRV: A Service Locator record is used to specify a combination of a host in addition to a port for a particular internet protocol or service.
- MX: The Mail Exchanger record is used to identify which hosts (servers or other devices) are responsible for handling mail for a domain.
In order to use a custom domain (sometimes referred to as a vanity domain) with Microsoft 365, you’ll need to add it to your tenant.
To add a custom domain, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the Microsoft 365 admin center (https://admin.microsoft.com) and log in.
- Expand Settings and select Domains.
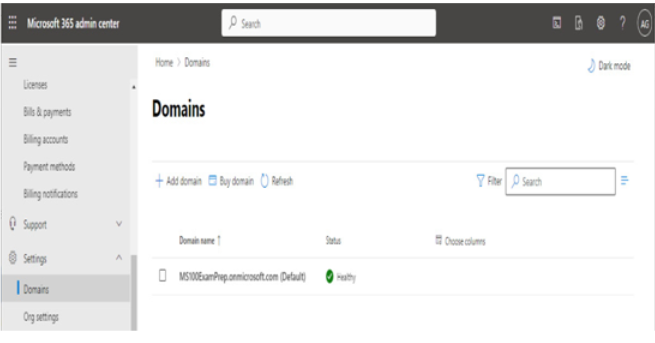
Figure 1.5 – Domains page of the Microsoft 365 admin center
3. Click Add domain.
4. On the Add a domain page, enter the custom domain name you wish to add to your Microsoft 365 tenant. Select Use this domain to continue.
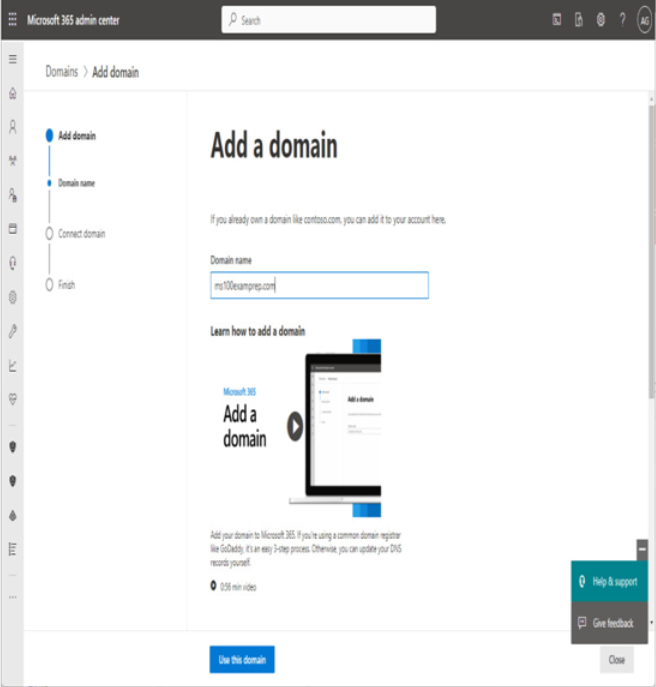
Figure 1.6 – Add a domain page